- Solid Mechanics: Solved Examples
SOM-KOM-DOM
Text-book Solutions
SOM, Solid Mechanics, Fracture Mechanics, Statics and Dynamics
This page addressess the analytical solution of text-books in the field of Strength of Materials, Solid Mechanics, Engineering Mechanics, Mechanical Vibrations, Kinematics & Dynamics of Mechanisms and Machinery...
Navier-Stokes Equation for Solid Deformation
Analogy between Solid Deformation and Fluid Flow
At the fundamental level, the governing equations of fluid mechanics ([relatively LARGER] deformation and kinematics of fluids particles) and structural mechanics ([relatively SMALLER] deformation and kinematics of solid particles) are equivalent.


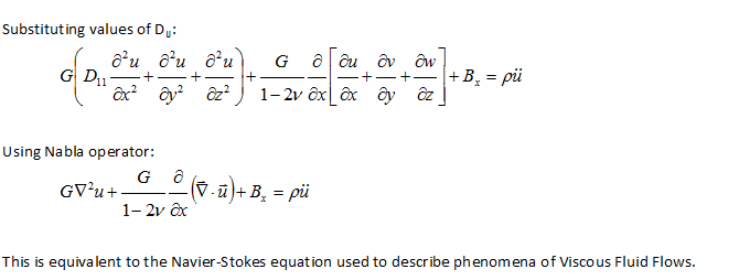
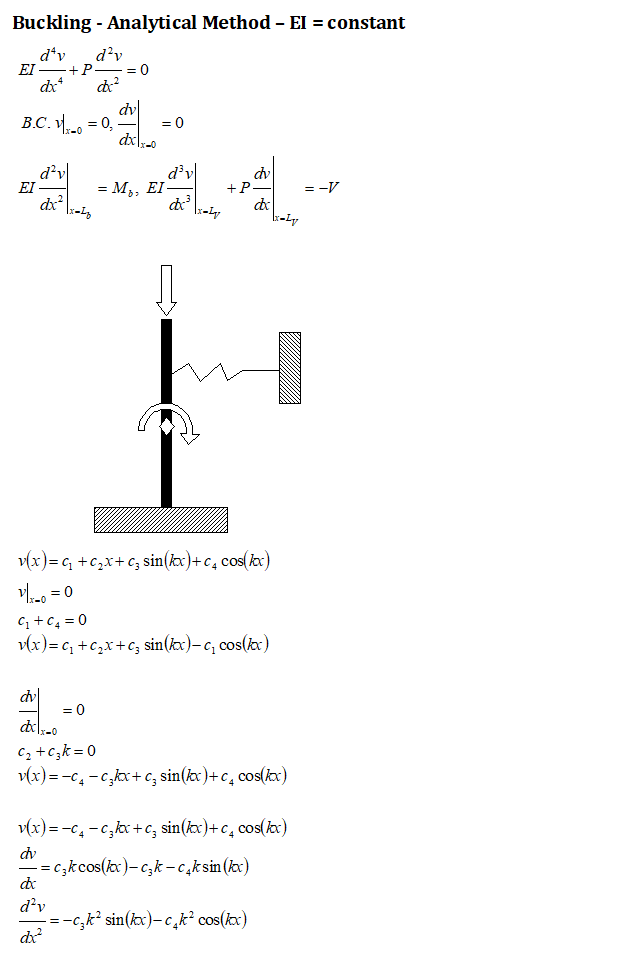
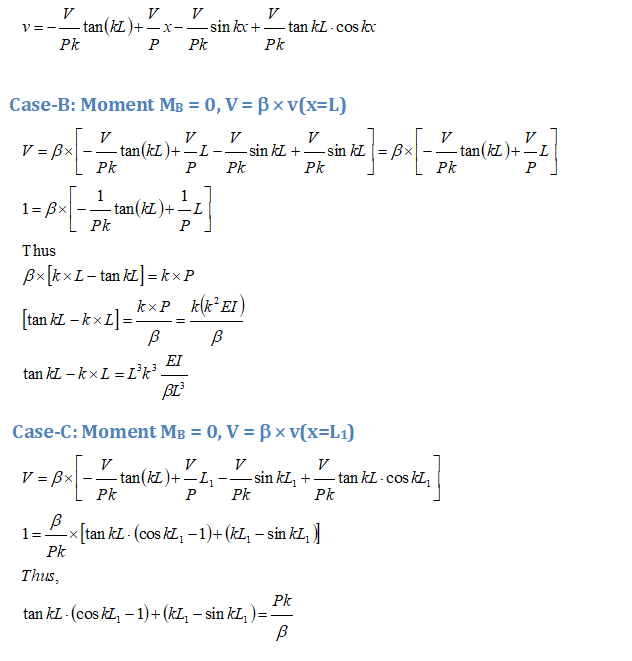
Buckling Calulation - Fixed Beam with Lateral Loads

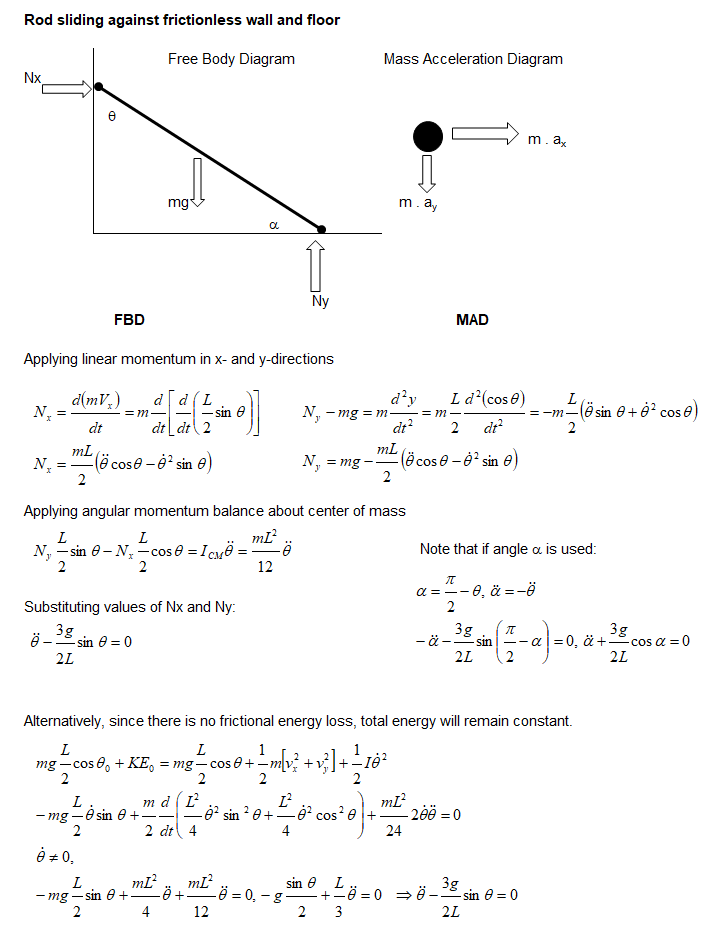
Rod sliding against frictionless wall and ground
While this problem may look trivial, the solution requires good experience in solving dynamics problem. The application of moment balance about sliding contact point will not yield desired result.
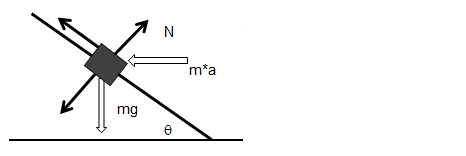
Direction of Reaction Force on Inclined Plane
This type of situation is very frequently encountered while solving statics and dynamics problems. What is the angle made by normal reaction with inclined plane or what is the component of gravity force perpendicular to the inclined plane? Just remember the theorem: "The angle between two lines is equal to angle between perpendicular to those lines".
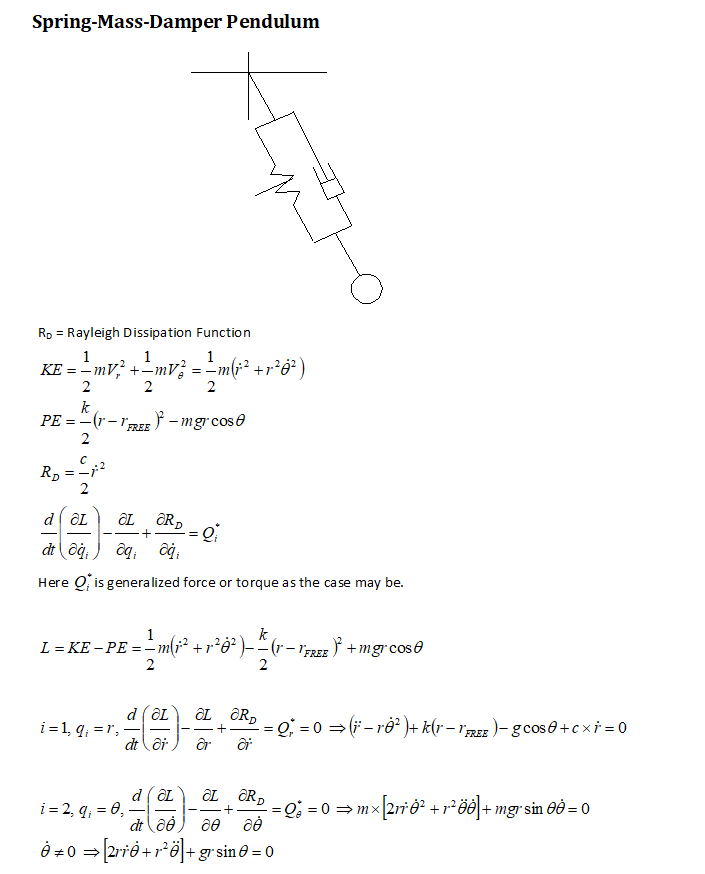
Mechanical Vibrations: Lagrangian Approach
Lagrangian approach is a powerful and straightforward method to derive equation of motion (EOM) for complex systems. The EOM for pring-mass-damper pendulum (also known as "sprung pendulum") is described below.
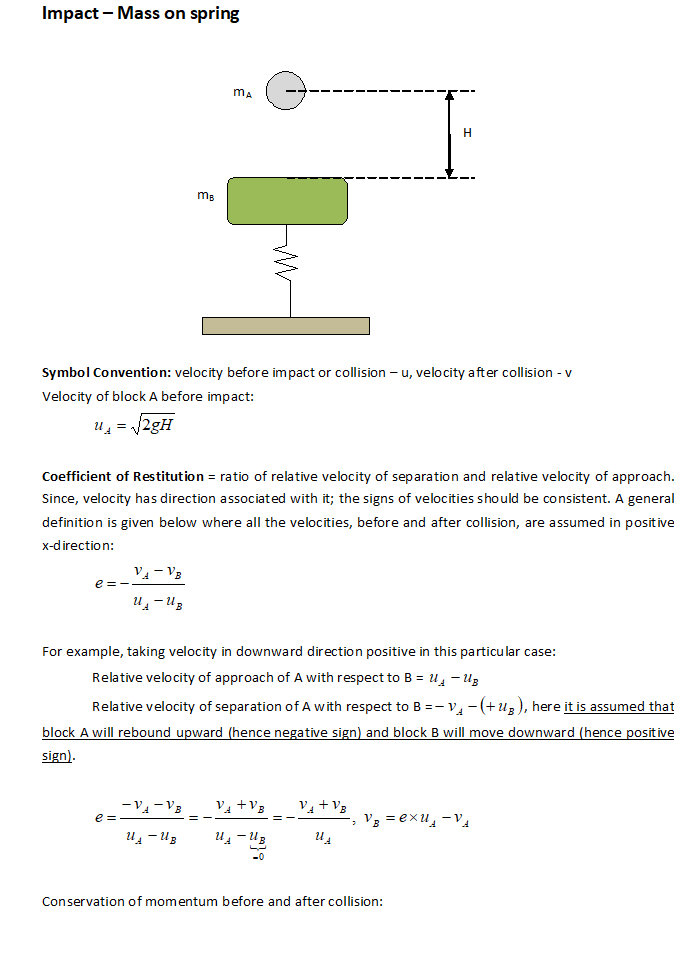
Inelastic Collision and Spring Compression
Collision is based on conservation of momentum and loss of energy defined by coefficient of restitution. This solution describes a case where one of the colliding objects is attached to a spring.
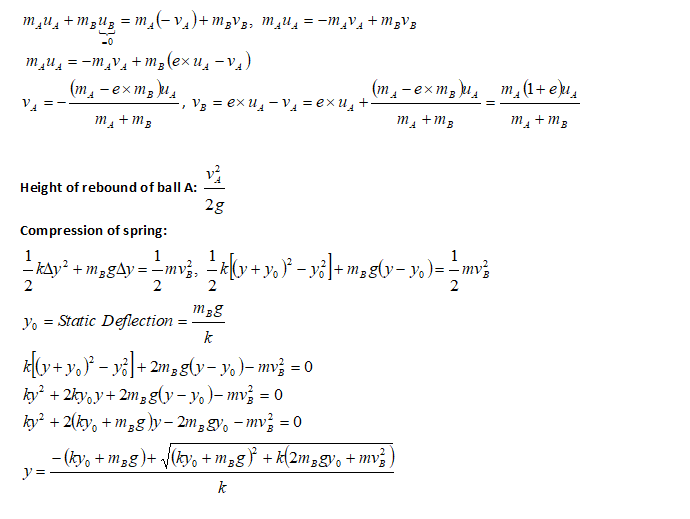
Crack Growth Calculations - Fracture Mechanics
Paris law is widely used in fracture mechanics calculations for number of cycles of variable loading required for crack to grow to critical size. Note that the rate of growth of crack per cycle, da/dN = A * δKm. Very often m is not an integer. The unit of δK is [MPa.m0.5]. Hence, special precautions should be taken to use consistent units for A, m and δK.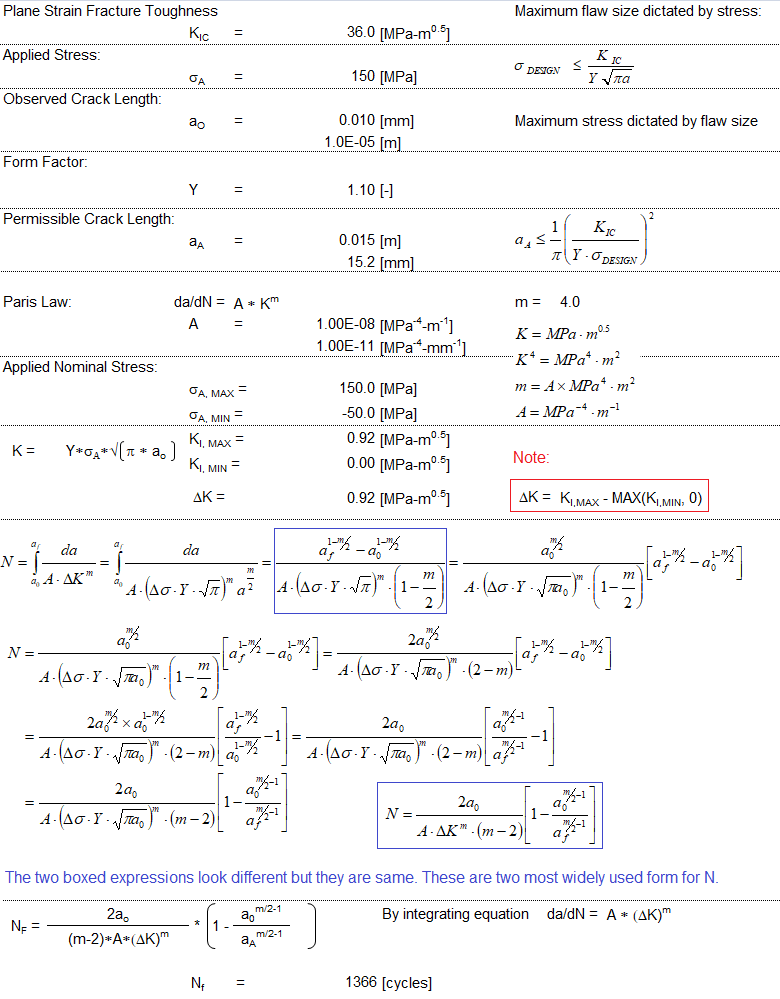
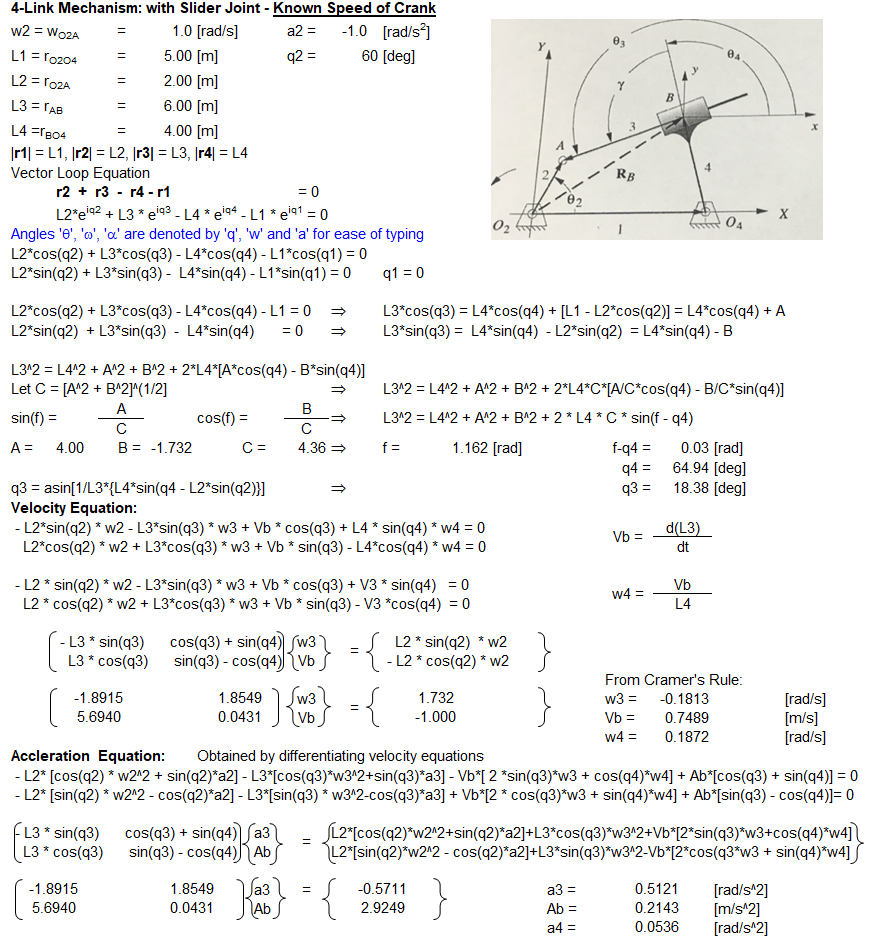
4-Bar Mechanism with Slider
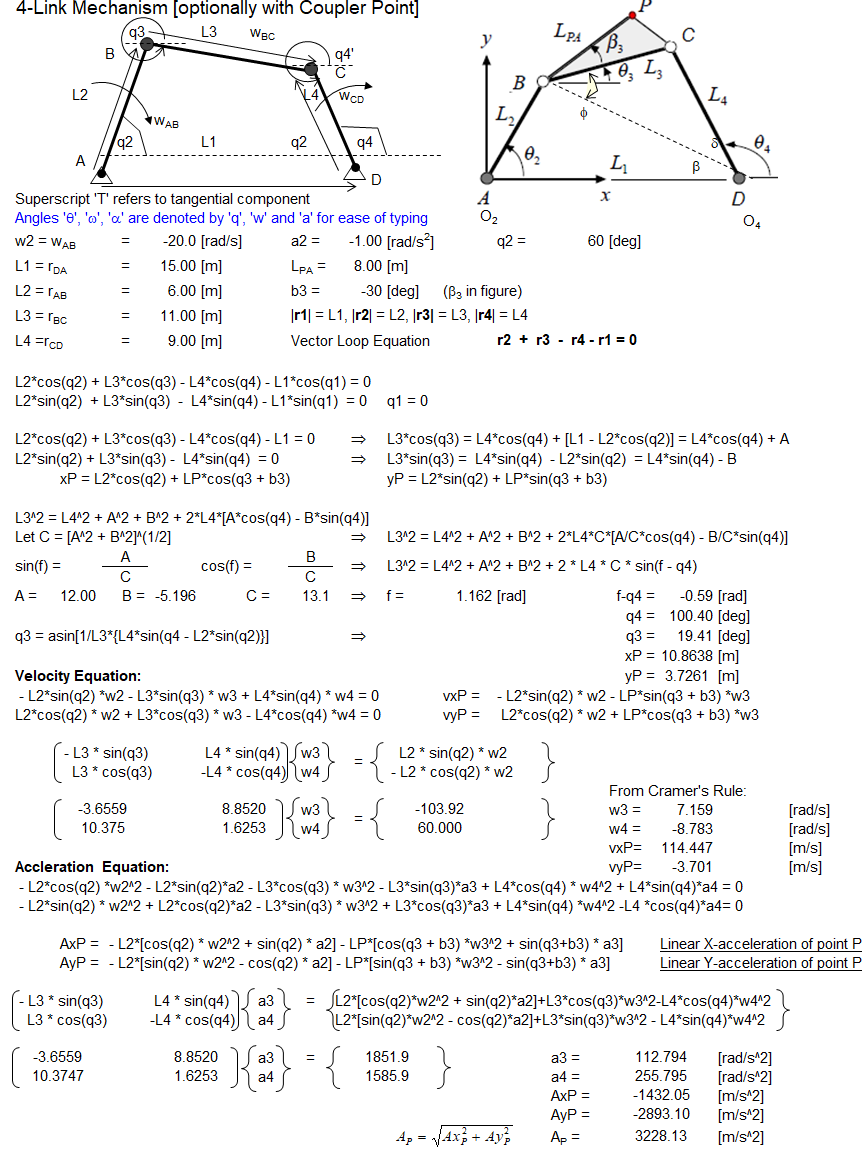
4-Bar Mechanism with Coupler Point
Slipping of Ladder
A ladder is leaning against a wall at certain angle having different coefficient of friction at wall and at the floor. The method to calculate maximum height a person of known weight can climb without slipping is described below.
Bending of Circulate Plates
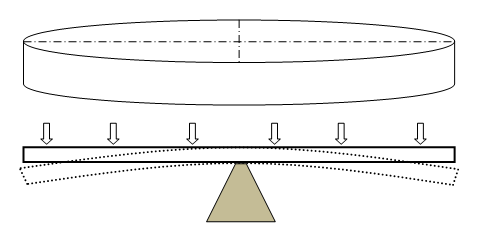
- Q = Transverse shear force [N/m]
- q = transverse distributed load intensity [N/m2]
- D = Flexural rigidity [N-m]
- w = out of plane deflection at any radius 'r' [m]
- R = Radius of the plate [m]
- t = thickness of the plate [m]
- E = Modulus of elasticity [Pa]
- ν = Poisson’s ratio
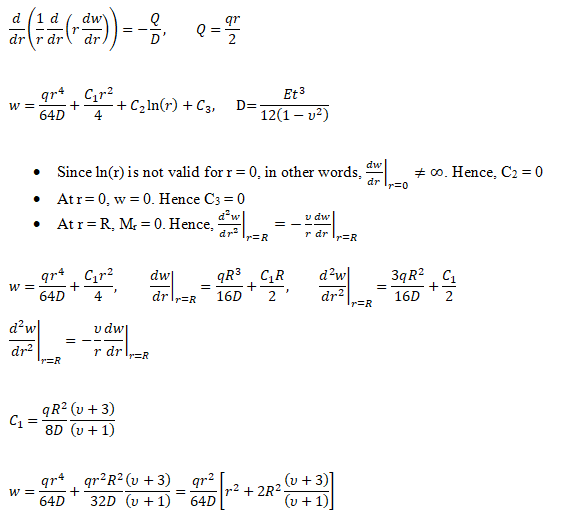
Strength of Materials: Book and Contents
The book by H. Timoshenko is considered as master-piece on this subject. The content of volume 2 are described below.





Some Solved Examples from the Book

Book on Fracuture Mechanics





Kinematics: Motions in Machines
The absolute motion analysis methods (also known as parametric method) requires specification of position s(P) of point of interest 'P' as a function of angle or Cartesion coordinates. Usually, sine or cosine rules are applied to derive an analytical equation. Chain rule is used while taking derivatives of the position to get instantaneous velocity and acceleration of point 'P'.The content on CFDyna.com is being constantly refined and improvised with on-the-job experience, testing, and training. Examples might be simplified to improve insight into the physics and basic understanding. Linked pages, articles, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to reduce errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content.
Template by OS Templates