- CFD, Fluid Flow, FEA, Heat/Mass Transfer
Shape Functions in FEA
FE Analysis
Shape Function
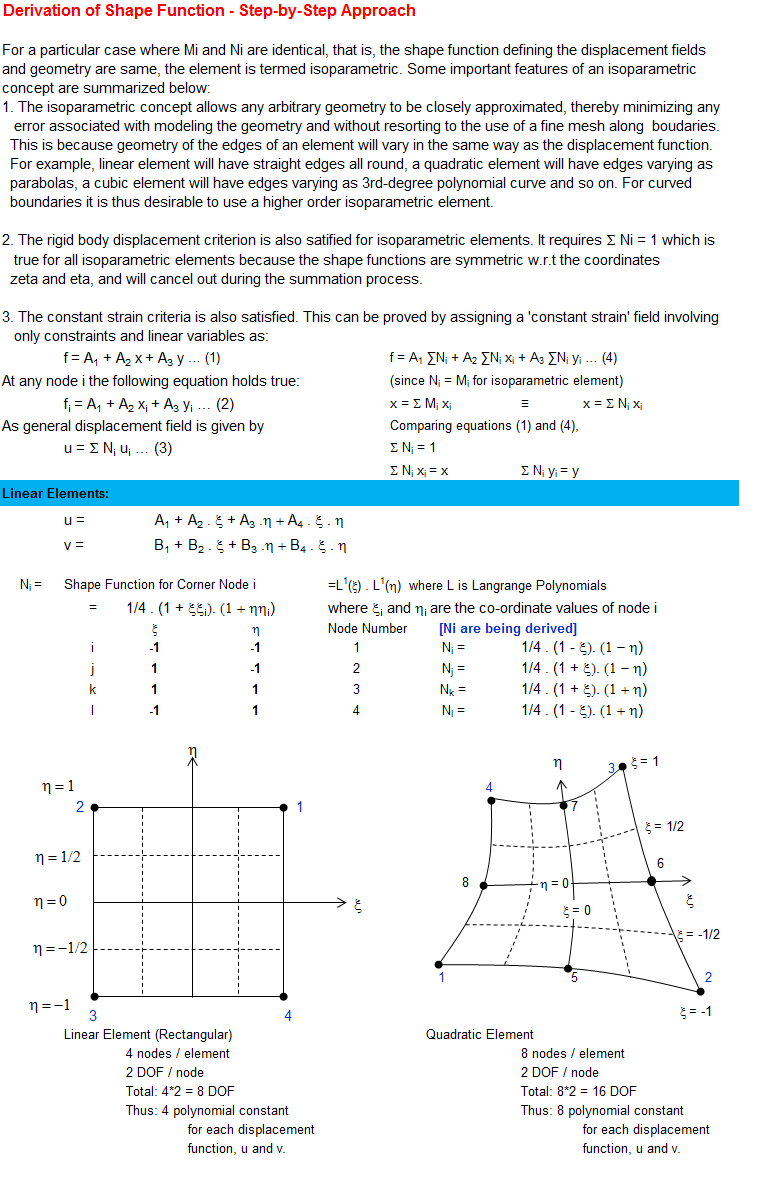
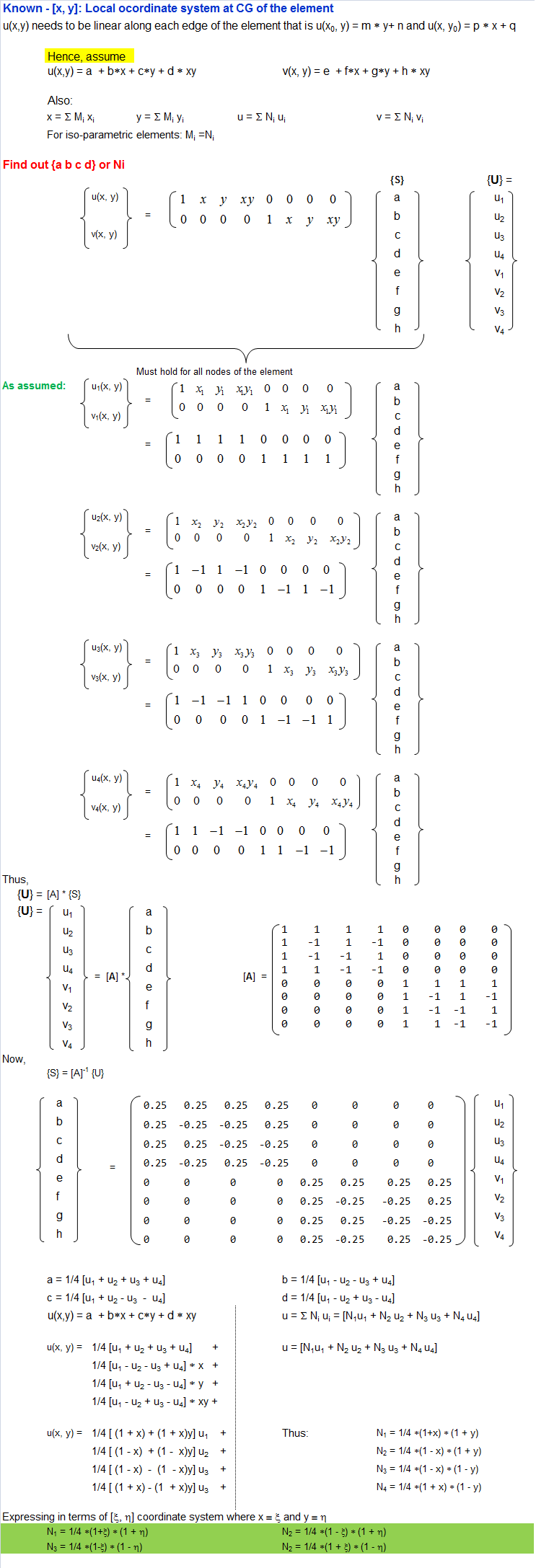
Shape functions are ubiquitous concept present in every Finite Element simulations of elastic components. This is an attempt to demystify the concept of shape functions by describing the step-by-step approach to get the function as they are used. The work is based on concepts presented in Zienkiewicz and Bathe where the authors have been [a bit extra] succinct in the textbook to describe the way shape functions are evolved.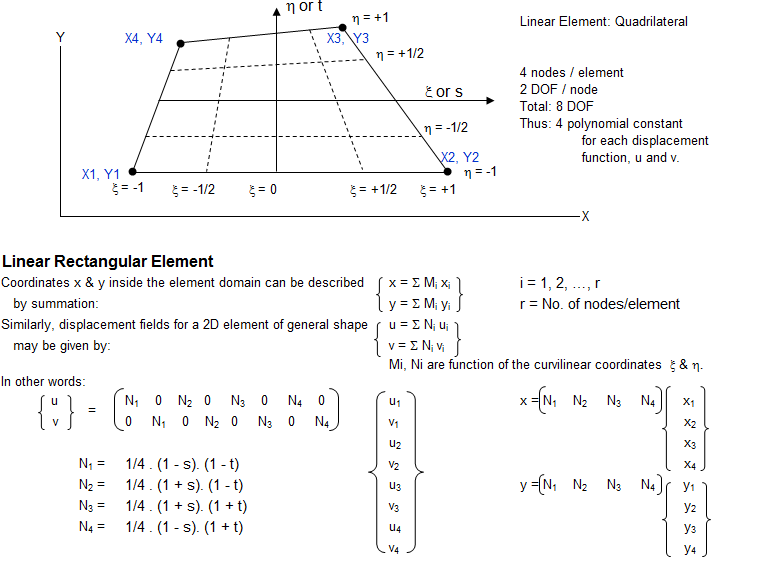
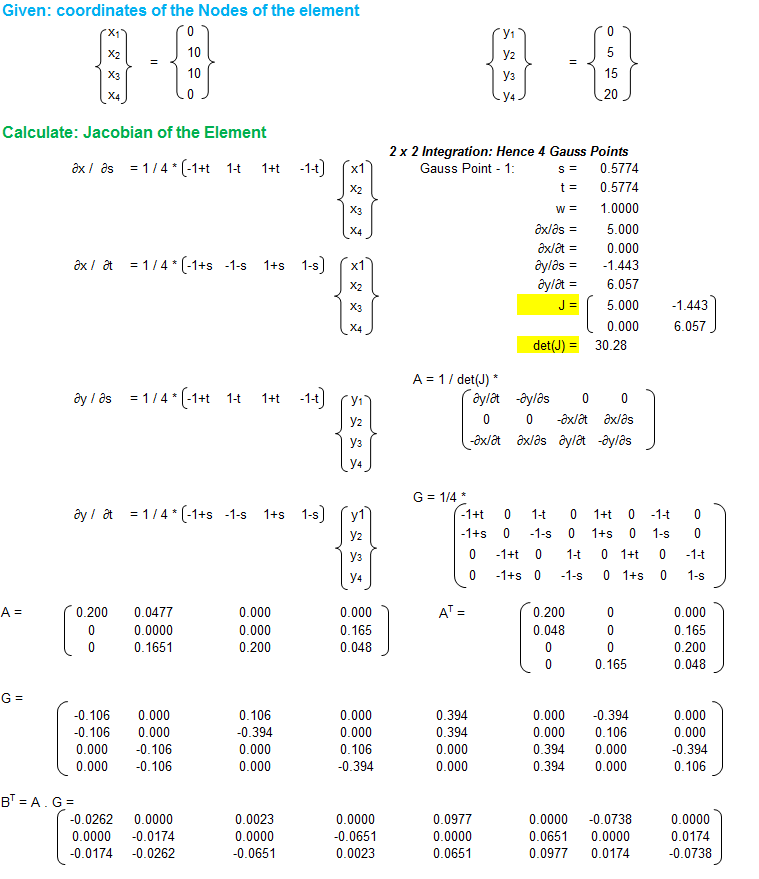
OCTAVE Scrip for Matrix Inversion
% Script for matrix inversion A = [ 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0, 1 -1 1 -1 0 0 0 0, 1 -1 -1 1 0 0 0 0, 1 1 -1 -1 0 0 0 0, 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1, 0 0 0 0 1 -1 1 -1, 0 0 0 0 1 -1 -1 1, 0 0 0 0 1 1 -1 -1 ]; inv(A)
Shape Function Example for 1D Quadratic Element
Obtain shape functions for the one-dimensional quadratic element with three nodes using local coordinate system -1 ≤ x ≤ +1.
O--------O--------O 1 2 3 -1--------0--------1------->x
Using shape function, any field (such as displacement, strain, stress) inside the element can be expressed as u(x) = ΣNiui where i = 1, 2, 3 for 3 nodes of the quadratic element. At nodes the approximated function should be equal to its nodal value. Thus:
u(-1) = u1, u(0) = u2, u(1) = u2From 3 points, we can fit a polynomial of order 2 that is a quadratic polynomial with 3 coefficients. Hence,
Let N1 = a1 + a2 * x + a3 * x2
N1(-1) = 1, → a1 - a2 + a3 = 1
N1(0) = 0, → a1 = 0
N1(1) = 0, → a1 + a2 + a3 = 0
Thus:a1 = 0, a2 = 1/2, a3 = -1/2
Finally,N1 = 1/2 * x *(x - 1)
Similarly,
Let N2 = b1 + b2 * x + b3 * x2
N2(-1) = 0, → b1 - b2 + b3 = 0
N2(0) = 1, → b1 = 1
N2(1) = 1, → b1 + b2 + b3 = 0
Thus:b1 = 1, b2 = 0, b3 = -1
Finally,N2 = x *(1 - x)
Similarly,
Let N3 = c1 + c2 * x + c3 * x2
N3(-1) = 0, → c1 - c2 + c3 = 0
N3(0) = 0, → c1 = 0
N3(1) = 1, → c1 + c2 + c3 = 1
Thus:c1 = 0, c2 = 1/2, c3 = 1/2
Finally,N3 = 1/2 * x *(1 + x)
The content on CFDyna.com is being constantly refined and improvised with on-the-job experience, testing and training. Examples might be simplified to improve insight into the physics and basic understanding. Linked pages, articles, references and examples are constantly reviewed to reduce errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content.
Copyright © 2017 - All Rights Reserved - CFDyna.com
Template by OS Templates